0spike
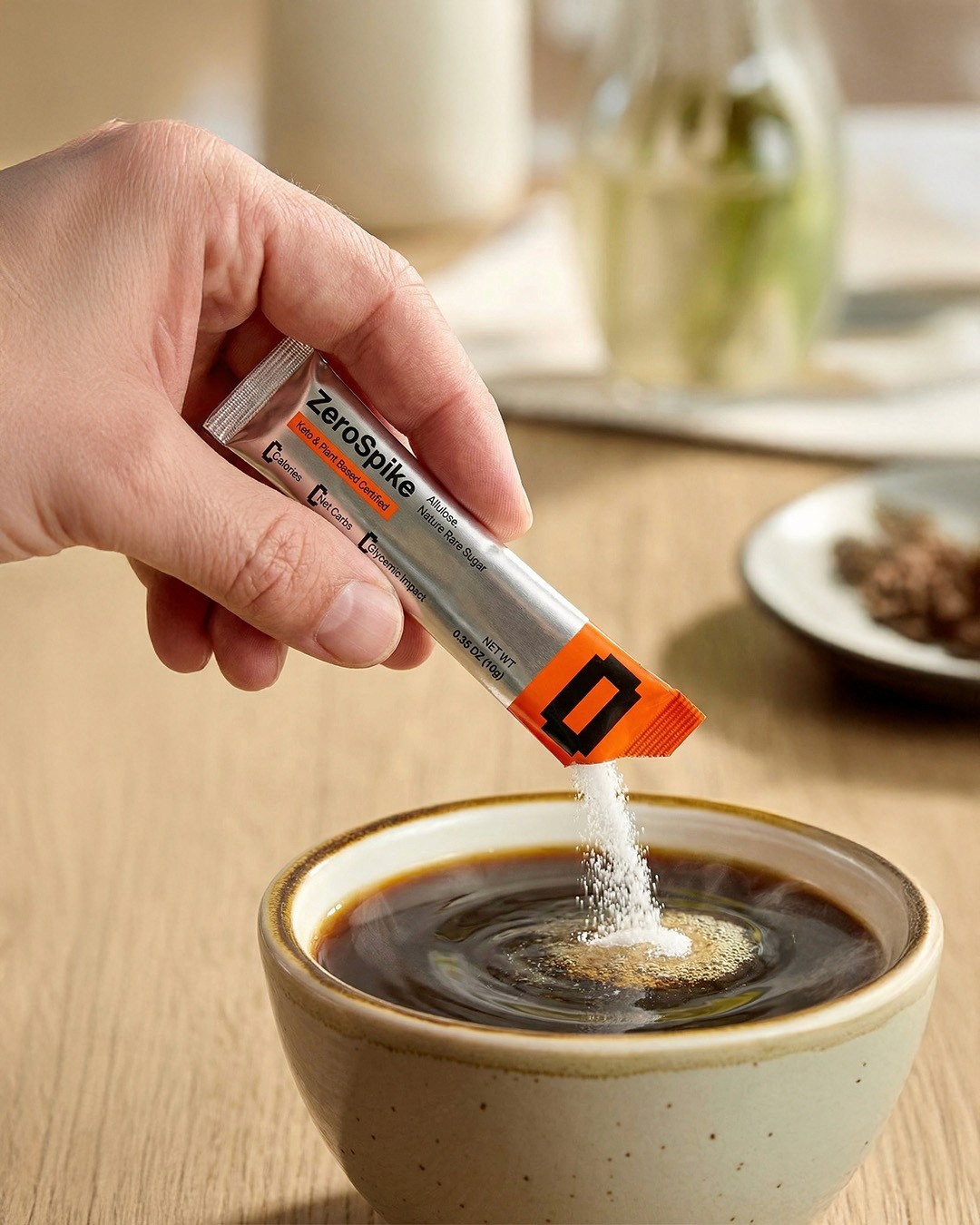
A rare sugar found naturally in figs and raisins. Your body absorbs it but can't metabolize it. Same taste. Zero glucose impact.
A rare sugar found naturally in figs and raisins. Your body absorbs it but can't metabolize it. Same taste. Zero glucose impact.
A rare sugar found naturally in figs and raisins. Your body absorbs it but can't metabolize it. Same taste. Zero glucose impact.






0+
0+
Trusted by health-conscious professionals across Singapore, Jakarta & Dubai
Trusted by health-conscious professionals across Singapore, Jakarta & Dubai
Trusted by health-conscious professionals across Singapore, Jakarta & Dubai
METABOLIC HEALTH
Backed by peer-reviewed research and trusted by professionals who optimize their health.
METABOLIC HEALTH
Backed by peer-reviewed research and trusted by professionals who optimize their health.
METABOLIC HEALTH
Backed by peer-reviewed research and trusted by professionals who optimize their health.


Allulose is a rare sugar your body recognizes but can't use for energy.
The result? You taste sweetness. Your glucose stays flat. No spike. No crash. No compromise.
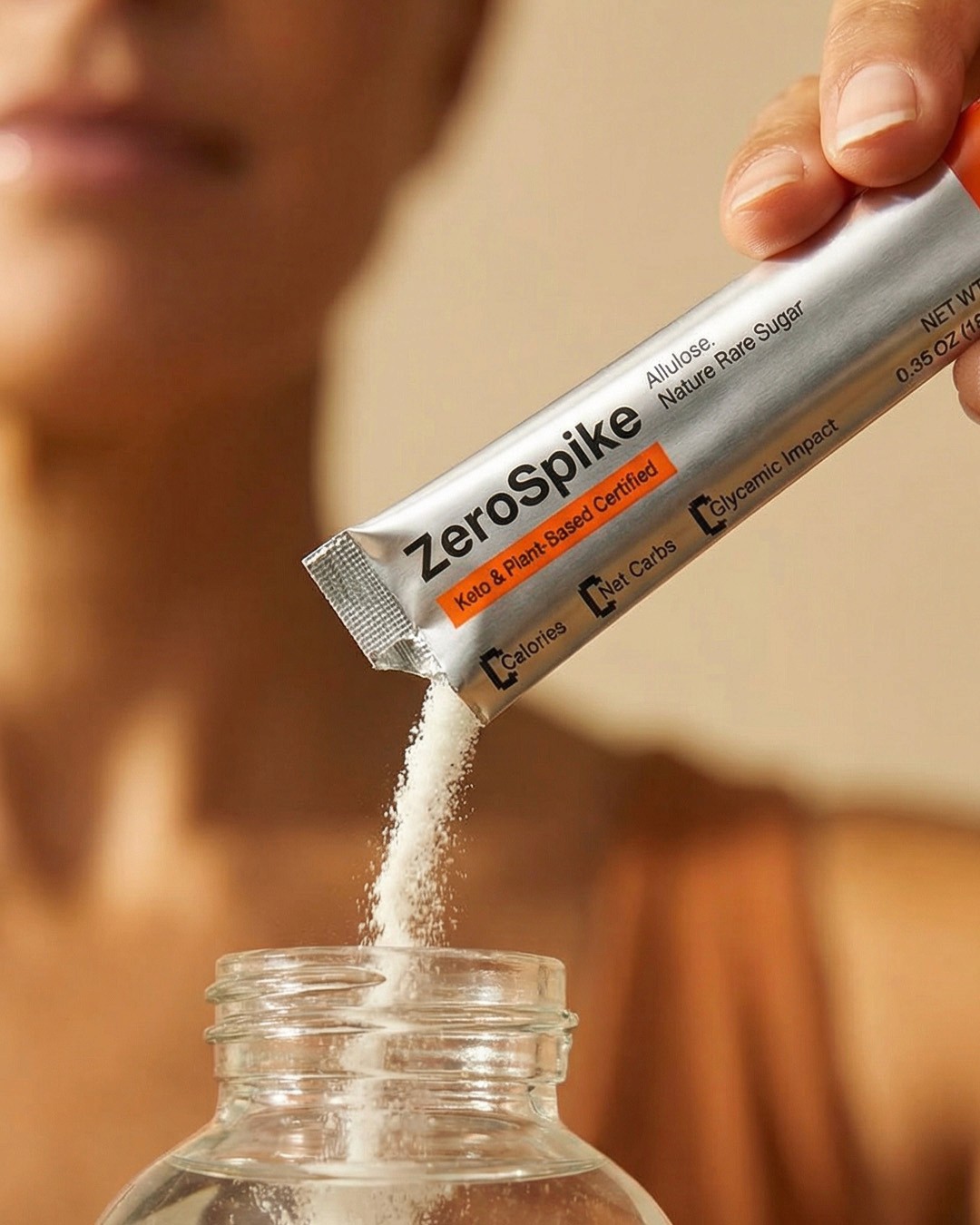






The Benefits
The Benefits
Explore What Makes
ZeroSpike Different

Zero Glycemic Impact
Clinical studies show allulose does not raise blood glucose or insulin levels. Your body absorbs it but lacks the enzymes to convert it to energy.
Naturally Occurring
Found in small amounts in figs, raisins, jackfruit, and wheat. Not artificial. Not synthetic. A rare sugar that exists in nature.
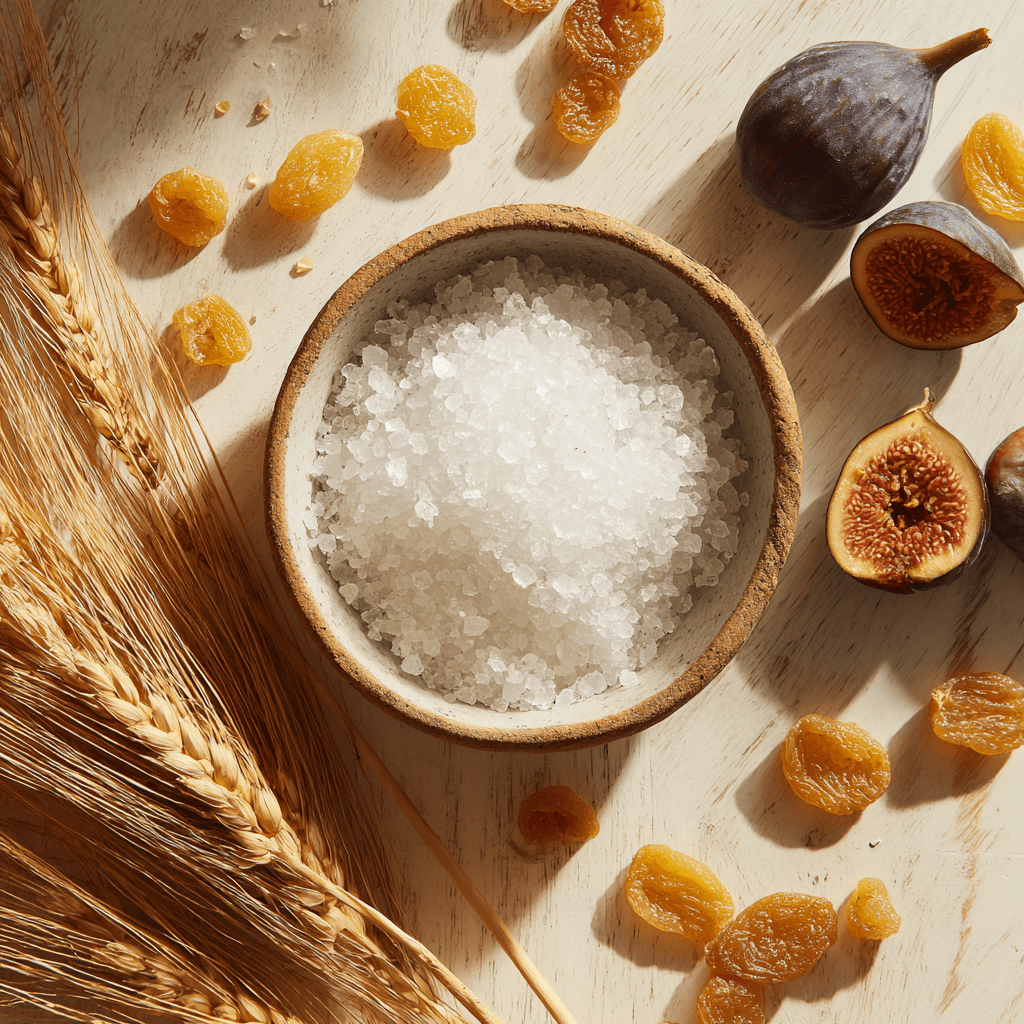


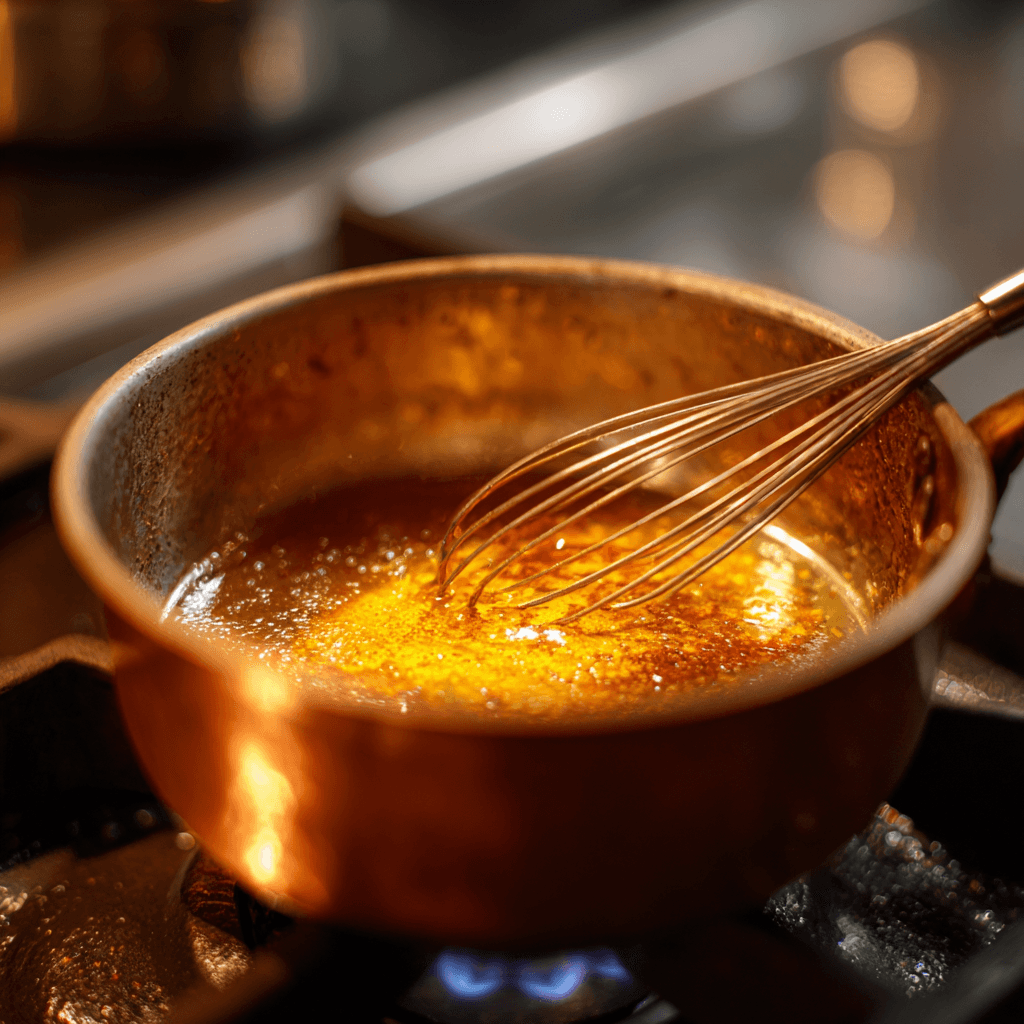

Tastes Like Sugar
70% the sweetness of table sugar with zero bitter or metallic aftertaste. Unlike stevia or monk fruit, allulose tastes like what it is: sugar. spending habits.

Works Everywhere
Dissolves in hot and cold. Caramelizes when heated. Works in baking, cooking, and beverages. Full functionality, zero glycemic cost.

Zero Glycemic Impact
Clinical studies show allulose does not raise blood glucose or insulin levels. Your body absorbs it but lacks the enzymes to convert it to energy.
Naturally Occurring
Found in small amounts in figs, raisins, jackfruit, and wheat. Not artificial. Not synthetic. A rare sugar that exists in nature.




Tastes Like Sugar
70% the sweetness of table sugar with zero bitter or metallic aftertaste. Unlike stevia or monk fruit, allulose tastes like what it is: sugar. spending habits.

Works Everywhere
Dissolves in hot and cold. Caramelizes when heated. Works in baking, cooking, and beverages. Full functionality, zero glycemic cost.

Zero Glycemic Impact
Clinical studies show allulose does not raise blood glucose or insulin levels. Your body absorbs it but lacks the enzymes to convert it to energy.
Naturally Occurring
Found in small amounts in figs, raisins, jackfruit, and wheat. Not artificial. Not synthetic. A rare sugar that exists in nature.




Tastes Like Sugar
70% the sweetness of table sugar with zero bitter or metallic aftertaste. Unlike stevia or monk fruit, allulose tastes like what it is: sugar. spending habits.

Works Everywhere
Dissolves in hot and cold. Caramelizes when heated. Works in baking, cooking, and beverages. Full functionality, zero glycemic cost.
...and more reasons to switch
...and more reasons to switch

FDA GRAS Status
Generally Recognized as Safe by U.S. FDA

FDA GRAS Status
Generally Recognized as Safe by U.S. FDA

Minimal Calories
Only 0.2-0.4 cal/g vs 4 cal/g for sugar

Minimal Calories
Only 0.2-0.4 cal/g vs 4 cal/g for sugar

No Aftertaste
Clean finish unlike artificial sweeteners

No Aftertaste
Clean finish unlike artificial sweeteners

Keto Compatible
Zero net carbs, fits ketogenic protocols

Keto Compatible
Zero net carbs, fits ketogenic protocols

Gut Friendly
Well-tolerated in moderate amounts

Gut Friendly
Well-tolerated in moderate amounts
ZERO




SPIKE
Benefit
Benefit
Experience The
Science of Sweet

Stable Energy
No more 3pm crash. Steady fuel all day.
When you consume regular sugar, blood glucose spikes then crashes. This cycle drains cognitive performance. Allulose provides sweetness without triggering the glucose-insulin rollercoaster.
Stable blood glucose levels
Consistent mental clarity

Stable Energy
No more 3pm crash. Steady fuel all day.
When you consume regular sugar, blood glucose spikes then crashes. This cycle drains cognitive performance. Allulose provides sweetness without triggering the glucose-insulin rollercoaster.
Stable blood glucose levels
Consistent mental clarity

Stable Energy
No more 3pm crash. Steady fuel all day.
When you consume regular sugar, blood glucose spikes then crashes. This cycle drains cognitive performance. Allulose provides sweetness without triggering the glucose-insulin rollercoaster.
Stable blood glucose levels
Consistent mental clarity

Metabolic Protection
Prevention is easier than reversal.
Repeated glucose spikes contribute to insulin resistance over decades. By the time most people notice, the damage has been accumulating. Allulose lets you enjoy sweetness while protecting your metabolic future.
Supports healthy glucose metabolism
No insulin spike response

Metabolic Protection
Prevention is easier than reversal.
Repeated glucose spikes contribute to insulin resistance over decades. By the time most people notice, the damage has been accumulating. Allulose lets you enjoy sweetness while protecting your metabolic future.
Supports healthy glucose metabolism
No insulin spike response

Metabolic Protection
Prevention is easier than reversal.
Repeated glucose spikes contribute to insulin resistance over decades. By the time most people notice, the damage has been accumulating. Allulose lets you enjoy sweetness while protecting your metabolic future.
Supports healthy glucose metabolism
No insulin spike response

Science-Backed Safety
Researched since the 1990s. Proven safe.
Allulose has GRAS status from the FDA. It's been used commercially in Japan since 2010. Peer-reviewed research consistently shows no adverse effects at normal consumption levels.
FDA GRAS approved
Decades of research

Science-Backed Safety
Researched since the 1990s. Proven safe.
Allulose has GRAS status from the FDA. It's been used commercially in Japan since 2010. Peer-reviewed research consistently shows no adverse effects at normal consumption levels.
FDA GRAS approved
Decades of research

Science-Backed Safety
Researched since the 1990s. Proven safe.
Allulose has GRAS status from the FDA. It's been used commercially in Japan since 2010. Peer-reviewed research consistently shows no adverse effects at normal consumption levels.
FDA GRAS approved
Decades of research
Statistics
Statistics
See The
Difference
0
0
Glycemic Index
0%
0%
Purity Level
0%
0%
Sweetness vs Sugar
0
0
Glycemic Index
0%
0%
Purity Level
0%
0%
Sweetness vs Sugar
0
0
Glycemic Index
0%
0%
Purity Level
0%
0%
Sweetness vs Sugar
How It Works
How It Works
How Allulose Works
In Your Body
1
Absorption
Allulose is absorbed in your small intestine, just like regular sugars. Your body recognizes it as a sugar molecule. So far, identical to glucose.
2
Non-Metabolism
Here's where the path diverges. Your body lacks the specific enzymes to convert allulose into energy. It simply doesn't get processed.
3
Excretion
70-84% of ingested allulose exits through urine within 24 hours. The remainder passes through your digestive system. All unchanged.
4
Zero Response
Because it's not metabolized, allulose doesn't trigger the glucose-insulin cycle. Your blood sugar stays flat. Stable energy. Clear thinking.
1
Absorption
Allulose is absorbed in your small intestine, just like regular sugars. Your body recognizes it as a sugar molecule. So far, identical to glucose.

2
Non-Metabolism
Here's where the path diverges. Your body lacks the specific enzymes to convert allulose into energy. It simply doesn't get processed.
3
Excretion
70-84% of ingested allulose exits through urine within 24 hours. The remainder passes through your digestive system. All unchanged.

4
Zero Response
Because it's not metabolized, allulose doesn't trigger the glucose-insulin cycle. Your blood sugar stays flat. Stable energy. Clear thinking.
1
Absorption
Allulose is absorbed in your small intestine, just like regular sugars. Your body recognizes it as a sugar molecule. So far, identical to glucose.

2
Non-Metabolism
Here's where the path diverges. Your body lacks the specific enzymes to convert allulose into energy. It simply doesn't get processed.

3
Excretion
70-84% of ingested allulose exits through urine within 24 hours. The remainder passes through your digestive system. All unchanged.


4
Zero Response
Because it's not metabolized, allulose doesn't trigger the glucose-insulin cycle. Your blood sugar stays flat. Stable energy. Clear thinking.
Testimonials
What Professionals Are Saying



4.8/5
Based on 14K+ reviews

Ahmad S
45, Jakarta, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Pije Maulana
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Pije Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
It has been a game-changer for my financial life. I love how it helps me stay organized my spending.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Cindy Maretha
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Aloy Ramadhan
Surabaya, Indonesia
I've been able to pay off debt, save for a down payment, and even start investing.
Testimonials
What Professionals Are Saying



4.8/5
Based on 14K+ reviews

Ahmad S
45, Jakarta, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Pije Maulana
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Pije Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
It has been a game-changer for my financial life. I love how it helps me stay organized my spending.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Cindy Maretha
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Aloy Ramadhan
Surabaya, Indonesia
I've been able to pay off debt, save for a down payment, and even start investing.
Testimonials
What Professionals Are Saying



4.8/5
Based on 14K+ reviews

Ahmad S
45, Jakarta, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Pije Maulana
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Pije Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
It has been a game-changer for my financial life. I love how it helps me stay organized my spending.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Cindy Maretha
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Aloy Ramadhan
Surabaya, Indonesia
I've been able to pay off debt, save for a down payment, and even start investing.

Ahmad S
45, Jakarta, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Pije Maulana
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Pije Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
It has been a game-changer for my financial life. I love how it helps me stay organized my spending.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Cindy Maretha
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Aloy Ramadhan
Surabaya, Indonesia
I've been able to pay off debt, save for a down payment, and even start investing.

Ahmad S
45, Jakarta, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Pije Maulana
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Pije Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
It has been a game-changer for my financial life. I love how it helps me stay organized my spending.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Cindy Maretha
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Aloy Ramadhan
Surabaya, Indonesia
I've been able to pay off debt, save for a down payment, and even start investing.

Ahmad S
45, Jakarta, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Pije Maulana
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Pije Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
It has been a game-changer for my financial life. I love how it helps me stay organized my spending.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Maulana
Surabaya, Indonesia
As someone managing type 2 diabetes, finding a sweetener that doesn’t raise my glucose has been a struggle. 0Spike Allulose lets me enjoy desserts again without guilt or spikes. It’s honestly life-changing.”

Cindy Maretha
Bali, Indonesia
I've finally taken control of my finances. It's so easy to use and has helped me save more money than ever before.

Rafliansyah R
Surabaya, Indonesia
The app is intuitive and easy to navigate, and it's helped me reach my financial goals faster than I ever thought possible.

Aloy Ramadhan
Surabaya, Indonesia
I've been able to pay off debt, save for a down payment, and even start investing.
FAQ
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
What is allulose?
Allulose is a "rare sugar" found naturally in small quantities in foods like figs, raisins, and maple syrup. Chemically, it is almost identical to fructose (fruit sugar), but its atomic structure is arranged slightly differently. This tiny difference completely changes how the human body processes it.
Is allulose natural or artificial?
Allulose is considered a naturally occurring rare sugar. It’s often produced from natural sources such as corn or sugar beets using an enzymatic process.
How does allulose taste compared to sugar?
Allulose has about 70% of the sweetness of regular sugar, with a clean, natural taste and no bitter aftertaste—unlike many artificial sweeteners.
How many calories does allulose have?
Allulose provides only 0.2–0.4 calories per gram, which is about 90% fewer calories than sugar.
Is allulose safe?
Yes. Allulose is recognized as safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and approved for use in many countries. Studies show it’s well tolerated when consumed in normal amounts.
What is allulose?
Allulose is a "rare sugar" found naturally in small quantities in foods like figs, raisins, and maple syrup. Chemically, it is almost identical to fructose (fruit sugar), but its atomic structure is arranged slightly differently. This tiny difference completely changes how the human body processes it.
Is allulose natural or artificial?
Allulose is considered a naturally occurring rare sugar. It’s often produced from natural sources such as corn or sugar beets using an enzymatic process.
How does allulose taste compared to sugar?
Allulose has about 70% of the sweetness of regular sugar, with a clean, natural taste and no bitter aftertaste—unlike many artificial sweeteners.
How many calories does allulose have?
Allulose provides only 0.2–0.4 calories per gram, which is about 90% fewer calories than sugar.
How do I sign up for the app?
Yes. Allulose is recognized as safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and approved for use in many countries. Studies show it’s well tolerated when consumed in normal amounts.
What is allulose?
Allulose is a "rare sugar" found naturally in small quantities in foods like figs, raisins, and maple syrup. Chemically, it is almost identical to fructose (fruit sugar), but its atomic structure is arranged slightly differently. This tiny difference completely changes how the human body processes it.
Is allulose natural or artificial?
Allulose is considered a naturally occurring rare sugar. It’s often produced from natural sources such as corn or sugar beets using an enzymatic process.
How does allulose taste compared to sugar?
Allulose has about 70% of the sweetness of regular sugar, with a clean, natural taste and no bitter aftertaste—unlike many artificial sweeteners.
How many calories does allulose have?
Allulose provides only 0.2–0.4 calories per gram, which is about 90% fewer calories than sugar.
Is allulose safe?
Yes. Allulose is recognized as safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and approved for use in many countries. Studies show it’s well tolerated when consumed in normal amounts.
Your daily rare sugar your body recognizes but can't use for energy.
We're so confident you'll love the clean, delicious taste of ZeroSpike


Your daily rare sugar your body recognizes but can't use for energy.
We're so confident you'll love the clean, delicious taste of ZeroSpike


Your daily rare sugar your body recognizes but can't use for energy.
We're so confident you'll love the clean, delicious taste of ZeroSpike


